Exploring Generative AI: A Clear Guide to its Capabilities, Limits and Future
Want to listen to this Article in/as a Podcast?
You’ve probably been hearing a lot about Artificial Intelligence (AI) recently, particularly something known as Generative AI. It’s a really popular subject right now, and there’s a good reason for that! But what exactly is it? How does it function, and why should you be interested? Well, that’s exactly what we’re going to find out in this article.
What is Generative AI?
Let’s get straight to the point. Generative AI is unlike the AI you may have encountered before. Older types of AI were mainly used for examining existing information. Think about things like organising data in a spreadsheet or spotting trends in a database. However, Generative AI is all about creating brand new content. It’s similar to giving an exceptionally clever and imaginative friend a set of tools and concepts, and then allowing them to develop something completely original.
This new form of AI can produce all kinds of content, from text and images to music, videos, and even code. It’s not just about analysis anymore; it’s about the act of creation itself. This technology is advancing rapidly, making it increasingly important for us to grasp what it is and how it might affect our lives. This guide will walk you through the main ideas behind generative AI, its various uses, and the ethical considerations we need to think about.
How Generative AI Developed
So, how did we get to this point? Well, early AI had limited capabilities. It was largely focused on crunching numbers and interpreting existing data. However, several key developments have paved the way for today’s generative AI:
• Transformer-based designs: These are revolutionary because they allow AI models to understand and generate intricate patterns within data. Think about how we, as humans, understand the context of a sentence – transformer models operate in a similar way.
• Increased processing power: Similar to how a more powerful computer helps you play complex games, greater processing capabilities enable AI models to learn more effectively and achieve more.
• Access to huge datasets: Because AI models learn from data, having access to massive datasets has greatly improved their abilities.
• The open-source movement: By openly sharing models and tools, innovation has been encouraged and more people have become involved.
All of these factors have contributed to the rise of generative AI models that can now produce realistic and compelling content.
Key Concepts in Generative AI
Now let’s delve into the specifics. Here are some essential concepts you should be aware of:
• Large Language Models (LLMs): These are the driving force behind many AI text-generation tools. Think of them as very sophisticated systems that predict the next word in a sequence. They are trained using vast quantities of data and learn to understand the nuances of language. Well-known examples include GPTs, Claude, and Gemini.
o LLMs utilise neural networks with billions of parameters to make predictions.
o They are trained on massive datasets using a process called self-supervised learning, which means they learn from the data itself, without needing specific labels.
• Key Technical Components: These models are powered by several crucial elements:
o The attention mechanism allows the models to concentrate on the most relevant parts of an input text.
o Embeddings are numerical representations of words that capture their meaning.
o Transformers process data simultaneously, making them incredibly efficient and powerful.
How Generative AI Functions
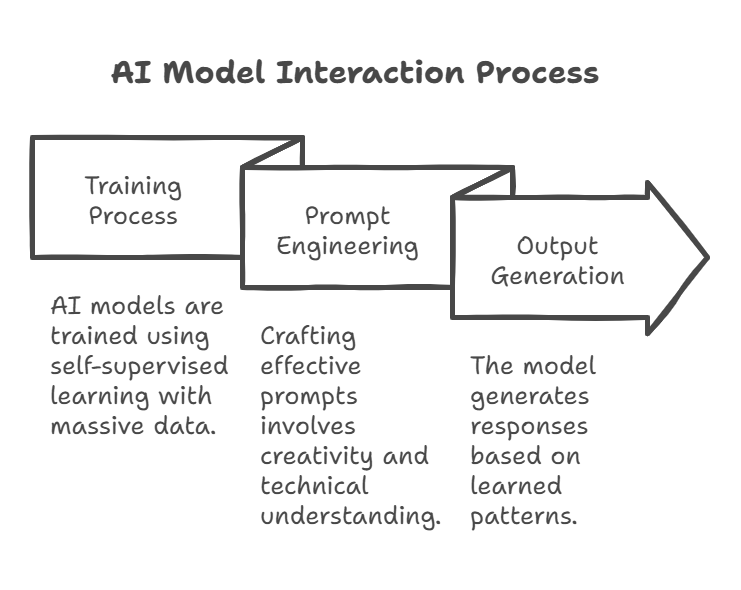
So, how does all this work in practice? Let’s break it down into steps:
• The Training Stage: AI models are trained using a self-supervised learning process. This is a resource-intensive task that uses enormous amounts of data.
• Prompt Engineering:
-This is essential for getting the desired results from these models. You need to learn how to write effective prompts.
-A good prompt will typically include instructions, context, input data, and specify the intended output.
-You can also adjust the temperature, which influences the creativity of the AI’s response.
-It’s often helpful to set the tone or context and even define a specific role for the AI, such as “act as a research analyst”.
– Adding examples can help guide the AI.
-You can also set restrictions and limitations, such as limiting the length of the response.
– Effective prompts are clear, specific, and concise, without ambiguous words.
-Prompt engineering is both an art and a science, requiring creativity and technical knowledge.
-Prompt engineering is an iterative process. You will need to experiment and adjust your prompts, while giving feedback to the model to get your desired result.
• Generating Output: The model analyses your prompt and creates a response based on what it has learned. The output could be text, code, an image, audio, or video, depending on the type of model.
Applications of Generative AI
Generative AI is now being used in many different fields:
• Content Creation: AI is helpful for writing blog posts, articles, social media content, and marketing materials. It’s also being used for creative writing and generating ideas.
• Software Development: Tools like GitHub Copilot help developers by suggesting code, assisting with documentation, and even identifying and fixing errors.
• Customer Support: AI-powered chatbots help businesses provide 24/7 customer service.
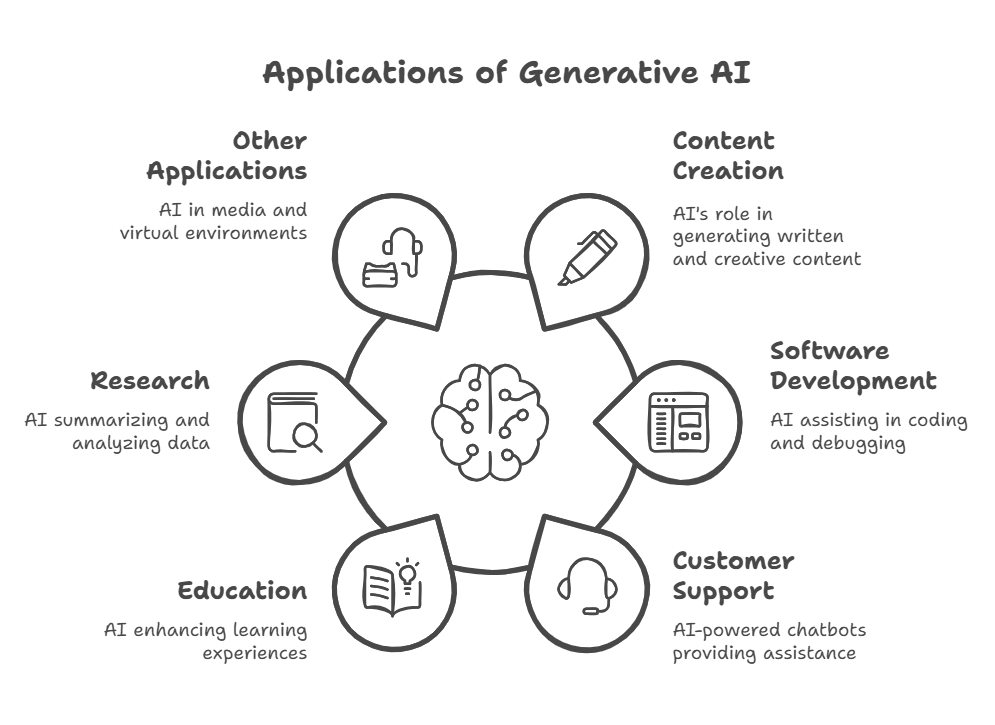
• Education: AI can provide personalised learning experiences and create customised study aids.
• Research: AI is used to summarise articles, extract crucial information, and analyse data.
• Other Applications: Generative AI is also used in areas like video and audio creation, virtual assistants, and creating virtual environments.
Ethical and Social Issues
It’s not all positive, though. There are some important things we need to consider when it comes to generative AI:
• Bias and Fairness: AI models can sometimes show the biases present in their training data. It’s crucial to use diverse and unbiased data when training these models.
• Misinformation and False Information: AI models can sometimes produce incorrect or nonsensical information. So, it’s important to always verify the facts, especially when relying on AI-generated information.
• Job Losses: There is a real risk that AI could automate some jobs. This means we need to think about retraining and helping people adapt to these changes.
• Copyright and Legal Matters: The legal framework for AI-generated content is not yet fully established. There are still many unanswered questions about copyright and ownership.
• Responsible Use: It’s vital to use AI ethically and responsibly. We need to avoid harmful uses and make sure AI is used to benefit society.
Advanced Methods and Future Directions
The world of AI is constantly changing! Here are some interesting developments to keep an eye on:
• Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG): This combines language models with external information to improve accuracy and provide context. It’s useful for reducing false information and providing up-to-date data, making it very helpful in virtual assistants and chatbots. RAG systems typically have a retrieval, ranking, and generation component.
• Function Calling: This enables an LLM to connect to external tools or functions.
• Chain of Thought Prompting: This technique is used for complex reasoning by breaking tasks down into steps.
• Multimodality: AI is becoming more versatile, working with text, images, audio, and video.
• AI Agents: AI agents have specific objectives and use different tools to help them achieve these. For example, they might be able to book tickets or create blog posts.
• Large Language Model Operating Systems (LLMOs): These place an LLM at the centre of a complete system, along with components like memory and agents.
• Decentralized AI: This focuses on using open-source models rather than relying on proprietary systems. This helps reduce dependence on specific companies and can improve data privacy.
Practical Examples and Demonstrations
Let’s look at some real-world examples:
• Code Generation Demo: Tools like GitHub Copilot can suggest code snippets and help with documentation.
• Text Generation Demo: Tools like Claude or ChatGPT can create creative text or summaries.
• Image Generation Demo: Models like Midjourney can produce images from a text prompt.
• Chatbot Demo: A simple chatbot with short-term memory can create a conversational experience.
• RAG demo: There are now many RAG systems available that can provide helpful answers from data sources, for example, SiteGPT.
Suggetion for Starting with Generative AI
Ready to get involved? Here’s some suggestions:
• Select the right tools: Various platforms and models are available, so choose the ones that best fit your needs. Check out platforms like Google Colab, OpenAI, and others.
• Experiment: Don’t be afraid to experiment with different prompts and AI models. The more you try, the better you will become.
• Keep learning: The world of AI is always changing, so it’s important to stay up to date with the latest advancements.
• Use Open Source AI: Many great open-source tools are available so you don’t have to depend on large corporations.
In Conclusion
So, that’s a comprehensive guide to generative AI. We’ve covered what it is, how it works, its various uses, and the ethical issues that need our consideration.
Generative AI is a powerful and rapidly growing technology that has the potential to transform many aspects of our lives. However, it is crucial that we use it responsibly, with an understanding of its limitations and potential consequences. We hope you feel prepared to explore this exciting field further and share your own experiences with the technology.
Thanks for reading, and happy experimenting with prompts!
